Router type PCB depaneling is the method whereby a router bit is set on a high revolution (~ 60,000rpm) spindle motor that moves on an X-Y axis by robotic arms and precisely grinds through connecting tabs of a printed circuit board. The router bit is specially designed for the PCB separating application in order to cut PCBs efficiently and control dust removal. The movement of router head is controlled by a computer driven servo-mechanism.
In the past, PCB routers were known for possessing slow process speed, complex programming and a large amount of dust generation. More recent routers are designed with programming capability utilizing a high-performance PC and integration of electronics with a mechanical system. PCB routers now come equipped with improvements in cutting speed, ease of programming, accurate cutting position control employing CCD camera on the spindle head and an effective dust collecting method.
Fig.2 Depaneled surface of PCB

Router depaneling

Rolling blade depaneling
Progress of Process Time by Optimized Head Speed Control
The movement speed of the spindle head at cutting and movement between cutting tabs are optimized and controlled by a computer program. While the controlled head speed at cutting is about 10 to 30mm/seconds which appears to be slow moving, it is only a small part of the total tact time. The distance between cutting tabs may be longer than the length of the tabs themselves and head moving speed between those tabs(faster than cutting speed) affect total tact time. Capability of optimizing head speed by computer programming shortens the depaneling process time.
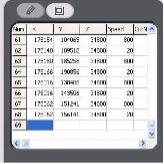
Fig. 3 Head speed setting
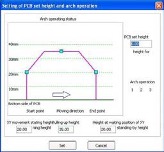
Fig. 4 Head movement setting
Furthermore, to minimize tact time, there are router models equipped with two jigs on a turn table in the machine. While a PCB is being cut on the jig in back side of machine, the operator is able to unload the cut PCB and load a new PCB on the jig simultaneously. After a new PCB is set in the front jig, the turn table rotates 180 degrees so that a cut PCB comes to front side to be removed and the new PCB will be cut in the back side of the machine.

Fig. 5 Jigs on a turn table
Easy Software Programming
A program can be easily created by the click and drag of a mouse operation on a Graphic User Interface drawing program for Windows XP operating system. The software provides copy, cut, paste, rotate and additional functions to ease programming for the operator. The created program is saved as a Windows file.

Fig. 6 GUI programming screen
Cutting of Curvilinear Designs on Variant Board
Many recent PCB designs require curvilinear outline. Programs utilizing software enable the operator to easily design cutting paths on the screen.

Fig. 7 Curvilinear cutting path
Efficient Dust-Collection
Historically, dust generated by routers created problems with cleanliness and reliability of the cut boards. Newer model PCB routers have been developed to deal with this problem. The dust generated at the time of cutting is drawn away from the bottom side of PCB by vacuum while at the same time dust is pushed out to the bottom by rotation of a specially designed router bit. The residual dust and is then sent to dust collector immediately.

Fig. 8 Bottom-side dust collecting system
Precise Cutting Position Control
Precise Cutting Position Control by Utilizing CCD Camera Precise and high-speed servo motor technology is commonly available. A CCD camera located at the spindle head enables the router machine to control its spindle head positioning quickly and accurately by utilizing fiducial marks on the PCB.

Fig. 9 Setting fiducial marks
Because a small error of circuitry could possibly cause a product recall in the market, preventing such failures is in strong demand. Recent PCB trends with its smaller board sizes and higher density of components have created a requirement for careful defect control in all aspects of the assembly process including depanelization. Lowering stress levels on PCBs including the depaneling process is an important factor in improving product yield and quality. Recent advancements in utilizing computer technology and integration of electronic/mechanical systems enable PCB routers to become faster and more versatile. With its low mechanical stress levels and precision cutting capability, PCB router depaneling process is recommended for high quality and high value PCB production.
Sayaka PCB Router Product Overview





