Testing method of a Capillary Flow Porometer
A Capillary Flow Porometry is a technique which is used in evaluating through-pore diameters of various porous materials. The equipment which uses this technique is called a “Capillary Flow Porometer (CFP)” and uses the bubble point and liquid displacement method to evaluate pore size of a filter media (ASTM F316, ASTM E1294). This technique is widely used in the industry for R&D of various functional porous materials and for the manufacturing process and quality control of final products.
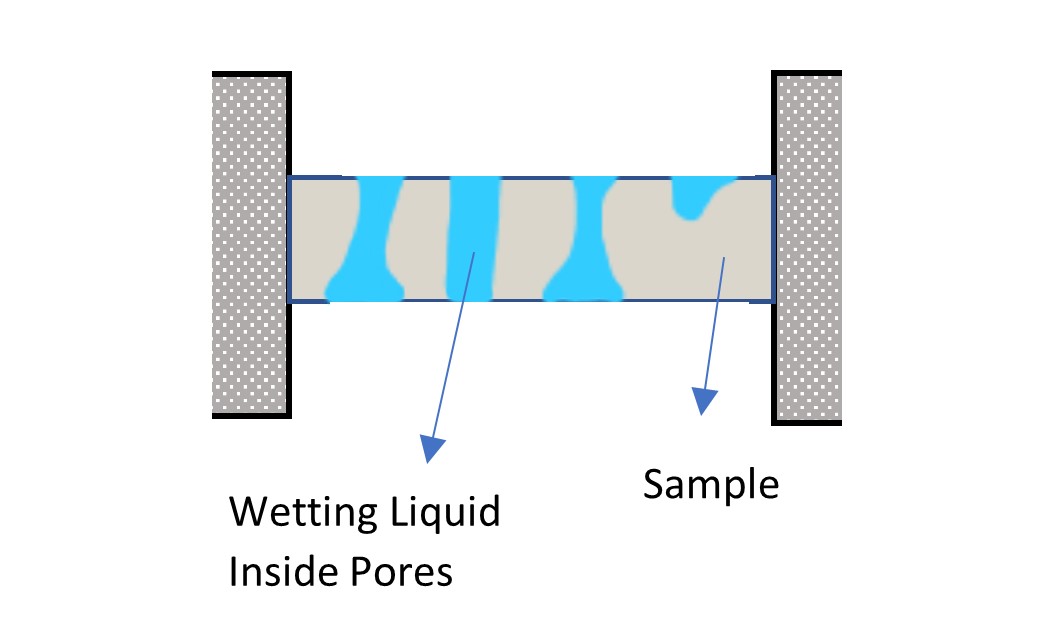
- A sample is immersed in a wetting liquid that completely fills the pores of the sample. The wetting liquid is retained within the pores of the sample due to capillary forces in the pores.
![TESTING METHOD OF A CAPOLLARY FLOW POROMETER1]()
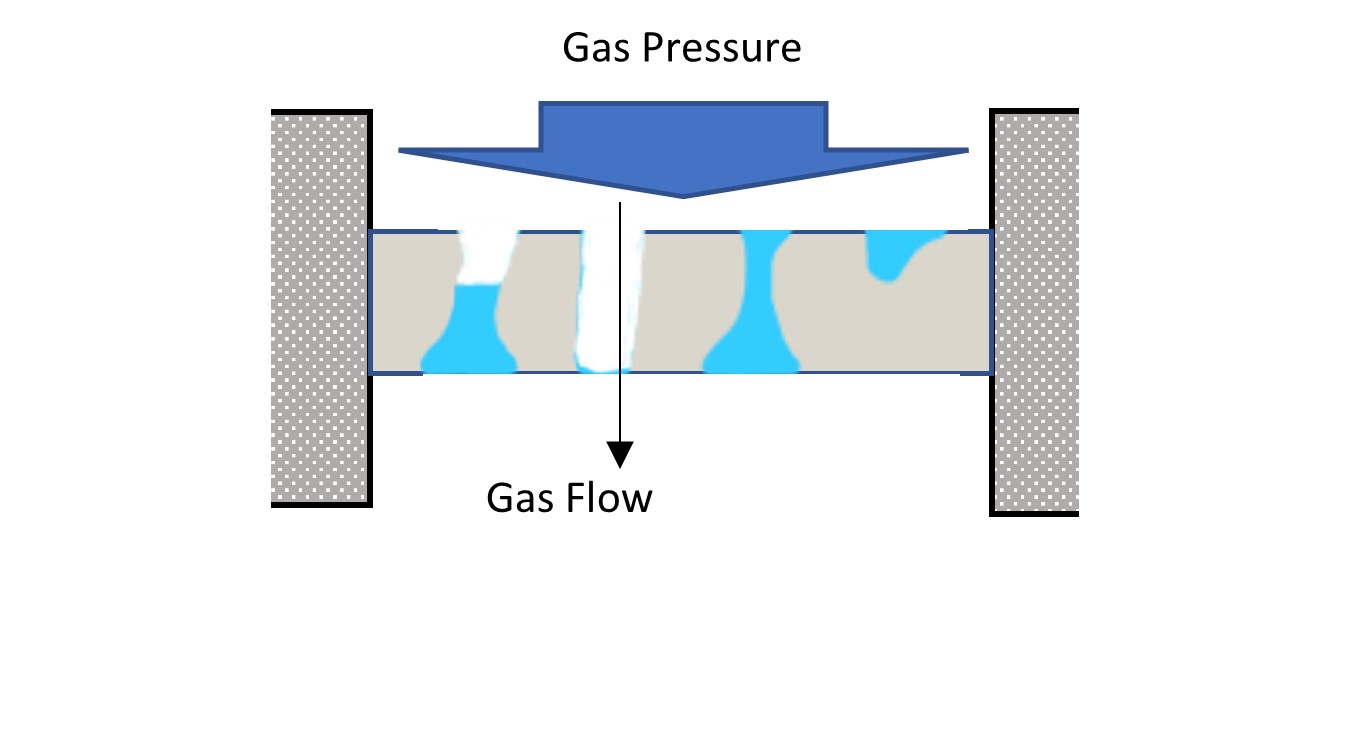
- The sample piece will be placed in a special designed cell and gas pressure will be introduced from one direction of the sample. The wetting liquid which fills the sample will retain inside its pores unless the gas pressure is high enough to overcome the capillary force. The pressure in which the pore gets pushed out by a specific gas pressure follows the below Washburn’s equation.
D=[4 γ cos θ]/PWhereas,
D: Pore diameter, γ: Surface tension of wetting liquid, θ: Contact angle P: Gas pressure - When the gas pressure is applied to the sample intermediately, the pore which has the largest through pore diameter within the sample will completely open up causing an gas flow which will be detected by the equipment (bubble point).
![TESTING METHOD OF A CAPOLLARY FLOW POROMETER2]()
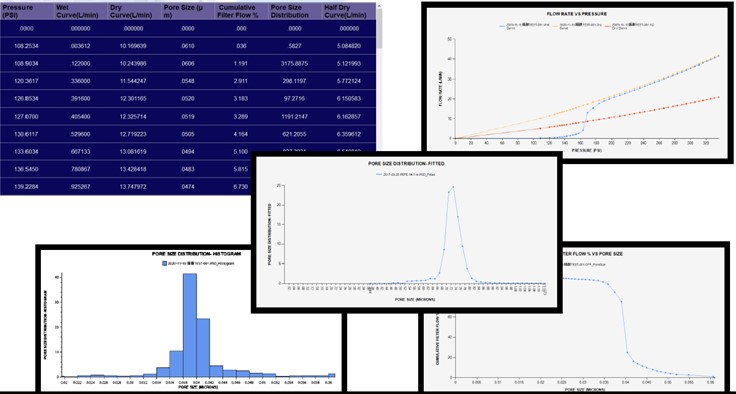
- After the largest pore within the sample is detected by air flow, gas pressure will continuously be applied to the sample. This will cause the pores to empty the liquid starting from the largest pore to the smallest pore corresponding to the pressure applied. The increase of the air flow will be measured simultaneously to calculate the through pore size distribution of the sample.
![TESTING METHOD OF A CAPOLLARY FLOW POROMETER3]()
Thinking about a through pore within the sample, the wetting liquid will not be pushed out from the pore unless the narrowest cross section (bottle neck) of the pore gets emptied from the pore. This aspect makes a CFP an ideal technique to evaluate the bottle neck through pore size distribution of a sample which is a crucial data in evaluating samples filtering/separating capability and gas/liquid permeability.